Birgitta Wöhrl

Prof. Dr. Birgitta Wöhrl
E-mail: birgitta.woehrl@uni-bayreuth.de
- Acting head of Biochemistry IV, University of Bayreuth (2018-2021)
- Associate Professor: Biochemistry IV, University of Bayreuth
- Habilitation: Biophysical Chemistry, University of Bayreuth
- Habilitation: Genetics, University of Osnabrück
- Doctoral Degree: Biology, University of Osnabrück
- Diploma: Biology, University of Regensburg
- List of Publications
Structure, stability and physiological function of PR-10 allergens
Globally about 250 million people suffer from food allergies. Many risk factors have been suggested to be associated with the development of allergies, i.e. environmental pollution, tobacco smoke, climate change, altered human gut flora due to nutritional changes etc. Although allergies in developed countries are still on the rise, no true treatment is available. The immune system of people suffering from food allergies combats small proteins existent in pollen, fruit or vegetables that are harmless. Antigen-specific IgE antibodies, together with one of the major effector cells of allergy, the mast cells are crucial for the development of the acute manifestations of these allergic disorders.
- Read more ...Hide
-
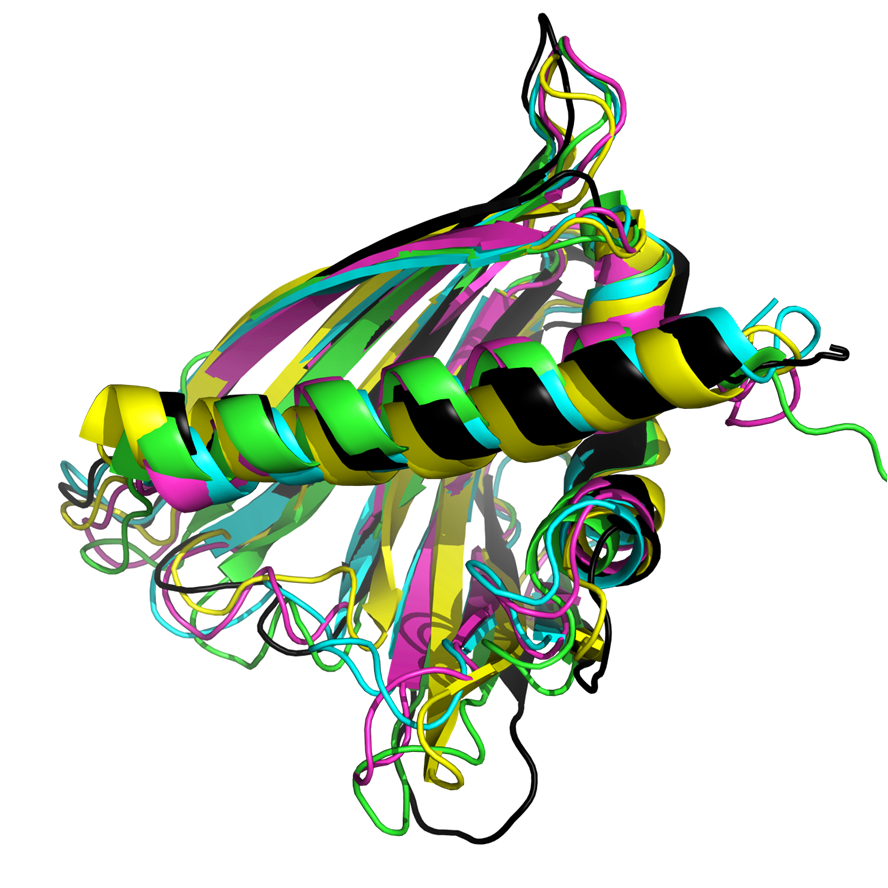
The so-called pathogen-related (PR-10) proteins are causative agents of food allergies. They are found in pollen of birch, alder and hazel, as well as in vegetables or fruits like carrot, celery, pear etc. In birch the most important allergy causing protein is the PR-10 protein Bet v 1. Among birch pollen allergic patients up to 70% develop so-called cross allergies to Bet v 1-homologue food allergens found in fruits or vegetables. These cross-allergies are caused by IgE antibodies that bind to similar or identical structural epitopes on the different allergens which share high structural homology.
Overlay of PR-10 allergen structures. Cor a 1.0401 (black), Bet v 1.0101 (blue, 1BV1), Fra a 1E (green, 2LPX) , Gly m 4 (yellow, 2K7H) and Pru av 1 (pink, 1E09)
Although they are present in many plants, knowledge on their functions is scarce. Our goal is to understand the structure and biological function of PR-10 proteins. To elucidate the function of PR-10 proteins we identify their natural ligands. For these purposes we isolate allergens from natural sources or use recombinantly expressed proteins. We apply various protein purification techniques, ligand extraction and use NMR, HPLC, mass spectrometry, CD spectrometry and biochemical and molecular biology techniques to investigate protein structure, ligand binding and to identify the corresponding ligands.